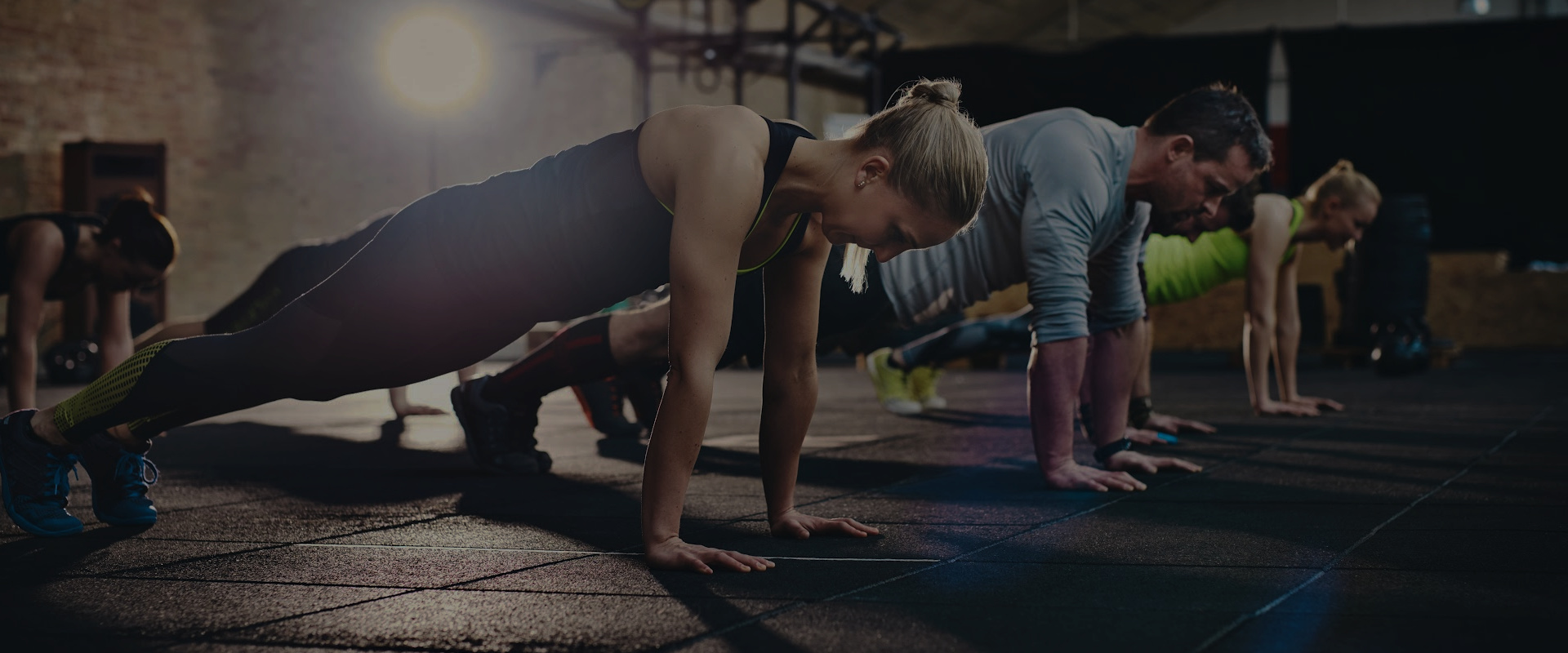


About HIITCore Fitness
HIIT + Core Strength = HIITCore®
Ready to get started on your fitness journey or just looking for a new gym to call home? HIITCore Fitness is the program you are looking for.
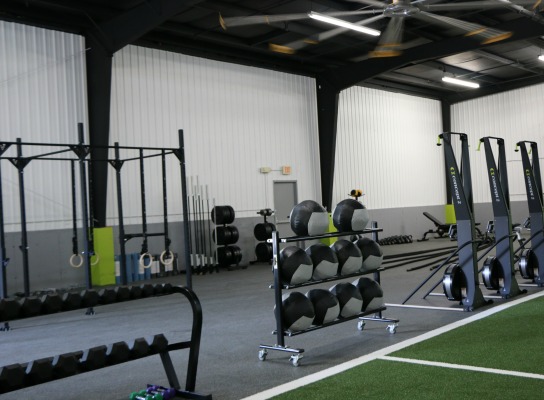

HIITCore Fitness is like no other! We specialize in HIIT & Core Strength Group Classes, Personal Training, Small Group Training, Corporate Wellness and Weight Loss Programs.
With over 5,000 square feet of open gym space, 75’x20’ large turf area (perfect for functional fitness), high density gym flooring, men’s and women’s bathrooms with showers, changing rooms, handicap accessible unisex bathroom with shower, private parking lot, and that’s not all…state of the art equipment such as Concept2 Rowers, Skiergs, AirBikes, AirRunner-self-powered treadmills and much, much more!!
We are located at 180 Allen Street Braintree, MA and 12 Garfield Cir. Burlington, MA.HIITCore FITNESS is comprised of a team of industry experts in Group Training, Nutrition, Cross Training, Functional Fitness, Weightlifting, and Personal Training.
Whether looking to increase general fitness capacity or specialize in Olympic weightlifting, traditional strength training, or gymnastics, the highly knowledgeable coaches at HIITCore are dedicated to helping every individual reach their goals.
Group member classes are offered daily and accommodate 12 individuals per class. Simply book in with MindBody, show up and get a great workout! Need more, choose from small group training or personal training, perfect for individuals who want personalized programming or want to learn highly technical movements. Truly something special, HIITCore Fitness is here to promote health and wellness to Braintree and surrounding communities.

HIITCore is a fusion of High Intensity Interval Training
with Core Strength & Conditioning.
The Benefits of HIIT
 HIIT workouts are great if you want to lose weight and build cardiovascular endurance. HIIT has been shown to burn more total fat than endurance training alone, so you’ll see that weight start coming off in no time. HIIT boosts favorable hormones, increases your metabolism and builds muscle giving you the tone look and increased stamina you’ve been looking for.
HIIT workouts are great if you want to lose weight and build cardiovascular endurance. HIIT has been shown to burn more total fat than endurance training alone, so you’ll see that weight start coming off in no time. HIIT boosts favorable hormones, increases your metabolism and builds muscle giving you the tone look and increased stamina you’ve been looking for.
The HIIT Effect
Whether you are male or female, young or old, studies have shown the wide-reaching effects of regular HIIT training workouts on the human body. Although results vary from one person to the next, people who regularly include HIIT in their training program have experienced many health benefits such as:
- Improved cardiovascular fitness
- Lowered risk of heart disease
- Increased insulin resistance
- Better HDL cholesterol levels
- Lowered systolic and diastolic blood pressure
- Fat release from both subcutaneous and intramuscular fat stores

The Science Behind HIIT
HIIT, High Intensity Interval Training, uses high intensity exercises for a brief period with short intervals of rest. Exercises can alternate quickly between upper and lower body movements, joints and various weight levels. This high paced workout with shorter recovery intervals places a greater demand on your muscles and better overall fitness results.
Energy is defined as a vigorous exertion of power or the capacity to do work. Work is defined as activity in which one exerts strength to do or perform something, or contracting muscles to apply force against a resistance. When you work out, you use your ability to channel energy to improve your fitness, ability or performance for weight loss, strength training or athletic competition.
Before your body expends energy, it needs to acquire fuel. Your body uses Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) as its own organic form of natural energy. ATP is stored in muscle cells and permits useful energy to be released, as in metabolism. ATP is also created through three different systems within your body: the ATP-Cr system, the Anaerobic system, and the Aerobic system.
When working out, the minimal stores of ATP in your muscles is depleted quickly as the load (weight) and intensity (repetitions) of your workout increases. Your body uses the ATP-Cr system to replenish ATP within the first 10 seconds of exercise. Then stored Phosphocreatine (CP) is broken down into Creatine (C) and Phosphate (P) in order to release phosphates. ADP (adenosine diphosphate) then collects the released phosphates to create ATP to provide energy for your workout. After 6-10 seconds, your Anaerobic system takes over.
The Anaerobic system takes over your body functions for the next 40-50 seconds—when your body is operating in an oxygen debt. The Anaerobic system works by breaking down glycogen, the stored form of glucose (sugar), in your muscles. Glycogen is released from the muscle and is used to resynthesized both ADP and phosphates. The absence of oxygen during glycogen breakdown creates lactic acid. When you increase your activity and the amounts of intense training, you also increase fatigue, as well as the need for both glycogen restoration and carbohydrate consumption.
Your Aerobic system “kicks in” to resynthesize ATP at around 60-80 seconds of exercise. This system is also used to resynthesize ATP during rests between higher intensity bouts of anaerobic exercise.
Your Aerobic system is the opposite of your Anaerobic system: it requires oxygen to resynthesize ATP through the breakdown of glycogen, fats, and protein. Therefore, an increase in your heart rate and breathing rate is required to transport oxygen into your muscle cells. Lactic acid is not a byproduct of the Aerobic system, despite using glycogen to resynthesize ATP. So, your body can now withstand a longer period of exercise (from 2 minutes–3 hours), but at a less intense level.
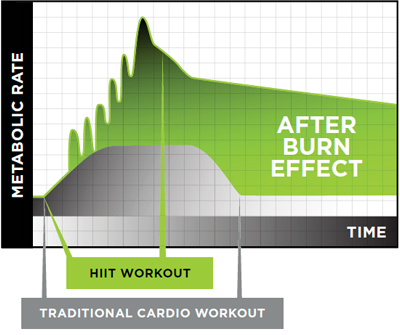
After a workout, your body will need to return to its pre-exercise levels of function. Excess post-exercise oxygen consumption, EPOC, uses oxygen to restore your body to its normal, resting level of metabolic function. EPOC, also known as the after burn effect, means that your body will continue to burn calories even after you’ve completed your workout.
EPOC replenishes the used muscle glycogen and aids in the rebuilding of muscle proteins damaged during exercise. The more intense your workout, the higher your EPOC will be, and the more calories your will burn. Because of the increased glycogen breakdown, taxing your anaerobic system during a workout puts a higher demand for oxygen to rebuild the used ATP both during your rest periods and after your workout.
For the best results, increase the intensity of your workout using these three simple methods:
